1.Global Electrification and Energy Transition Background
According to the latest Rho Motion data, global sales of fully electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles rose 23% in October 2025 to 1.9 million units, marking a record monthly high. China, Europe, and North America together accounted for over 90% of global EV sales, underscoring the accelerating pace of electrification worldwide.
At the same time, the IEA Global EV Outlook 2025 notes that charging infrastructure deployment continues to lag behind—global public charging points are growing at an annual rate of just 18%, less than half the pace of EV fleet expansion.
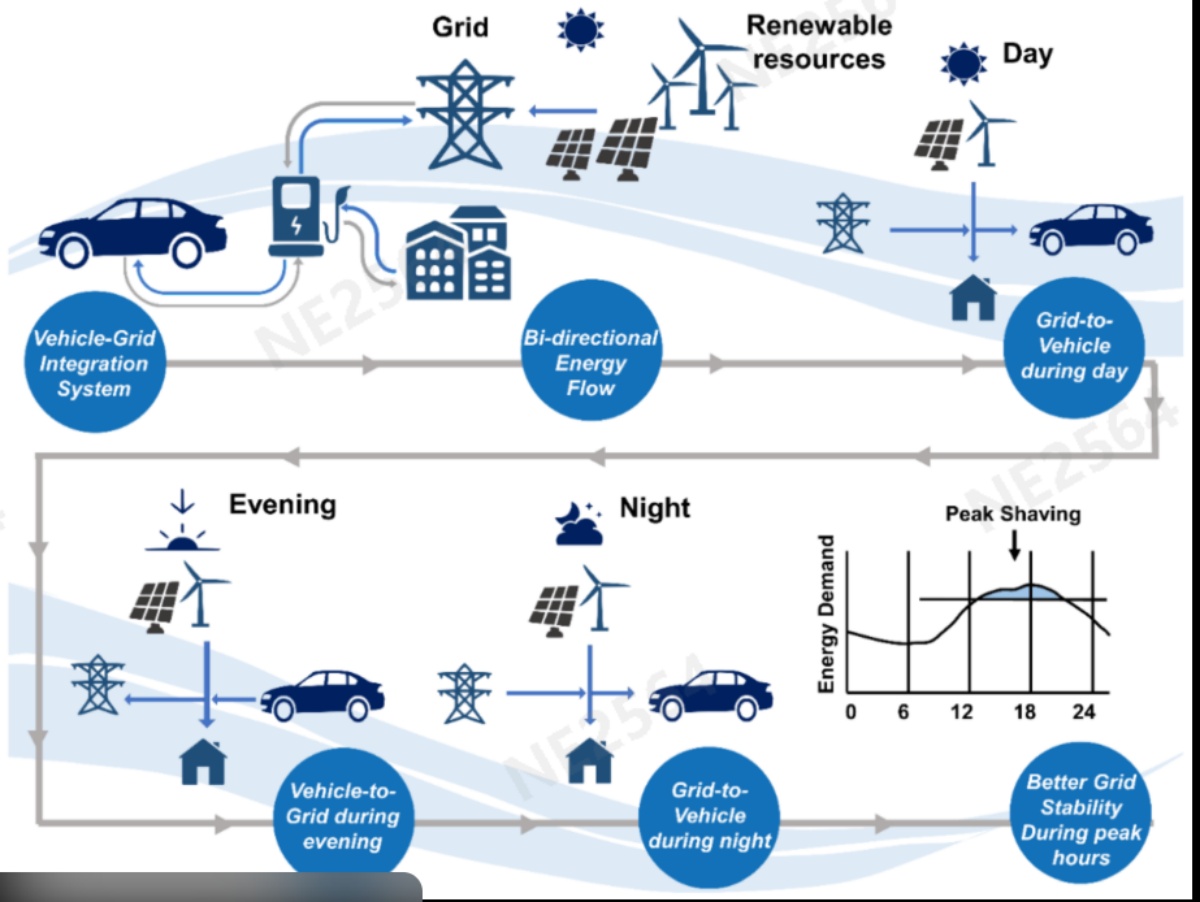
As high-power EV adoption expands and the energy mix shifts toward renewables, grid stress and peak-valley imbalances are becoming increasingly critical. Against this backdrop, battery- integrated V2G charging architecture is emerging as a pivotal solution, balancing grid stability, enabling bidirectional energy flow, and unlocking the next generation of ultra-fast charging technology.
2.Industry Pain Points
Despite promising growth, the EV charging market faces several challenges that impact the speed, cost, and efficiency of charging infrastructure deployment:
2.1 Grid Access and Hosting Capacity Constraints
Many charging installations are limited by local grid hosting capacity, aging low-voltage distribution networks are becoming bottlenecks, and insufficient investment in grid upgrades restricts the scale and pace of high-power charging deployment.Traditional ultra-fast chargers typically require large-capacity transformers and reinforced feeders, posing:
- Long wait times and high costs for grid connection upgrades
- Limitations on siting chargers where grid capacity is insufficient
- Requiring transformers causes extra installation cost
2.2 Lengthy and Fragmented Approval Processes
Across Europe, planning, construction, and grid connection approvals vary significantly between countries and regions. Some jurisdictions experience permitting cycles of 6 to 18 months, impeding fast market entry and scale. Policy and technical standards are fragmented within the EU, complicating cross-border deployment and scaling for operators.
2.3 Uneven Charging Station Distribution and Limited Fast Charging Coverage
Although the number of public charging points is increasing, only about 13.5% of European chargers exceed 22 kW fast charging capability, resulting in coverage gaps and regional disparities.
Certain countries dominate the charging infrastructure landscape, while others remain under-served, creating a market environment where high-power, rapid deployment charging stations.
2.4 Residential and Multi-Unit Dwelling Charging Challenges
Approximately 45% of Europe’s population lives in apartment complexes, where installing charging infrastructure faces unique hurdles:
- Complexities in power access and wiring within shared parking areas
- Ambiguities in responsibility and cost-sharing among landlords, tenants, and property managers
2.5 Commercial Model Risks and Return on Investment Uncertainty
Despite robust EV sales growth, charging station utilization remains variable, operational costs are high, and profitability models are not yet fully mature. Some public charging sites struggle with low usage and elevated maintenance expenses.
3.Highlights of Battery-Integrated V2G DC Charger (Nepower)
Nebula’s Battery-Integrated V2G DC Charger stands out with innovative technologies and system optimizations, featuring key highlights that drive breakthroughs in next-gen ultra-fast charging:
189kWh Integrated Battery: CATL’s high power LFP battery,extreme safety
40/80kW Input: No transformer upgrade, flexible & rapid deployment
200-1000 VDC :Compatible with mainstream models in the market
Dual Liguid-Cooling System: High durability& low noise, 10+ years lifespan
Modular Design: Easy O&M, reduce labor costs
Advanced V2X Technology: Smart bidirectional energy management, maximize ROI
270kW Ultra-Fast Charging: 80km range in 3 minutes, satisfying the demand for fast charging
4.Technical Data Sheet: Excellent System Performance
| Input | |
| Input power supply | 3W+N+PE |
| Rated input voltage | 400±10%V AC |
| Rated input power | 40/80 kW |
| Rated input current | 150A |
| Rated AC frequency | 50/60HZ |
| Output | |
| Max output charging power | One vehicle charging:270kW (Max); Two vehicle charging:135kW/EV (Max) |
| Charging voltage range | 200V~1000V DC |
| Charging current | 300A (400A for short-time) |
| No. of charge connectors | 2 |
| Exposed charging cable length | 5m |
| Basic characteristics | |
| Dimension (W*D*H) | 1800*1450*2160mm |
| Weight | ≤2600kg |
| Product life cycle | >10 years |
| Communication protocol | OCPP |
| Energy storage capacity | 189kWh |
| Noise | ≤55dB @25°C |
| IP rating | IP55 |
| Storage ambient temperature | -30℃~60℃ |
| Working ambient temperature | -25℃~50℃ |
| Cooling method | Liquid-cooling |
| Payment methods | Credit card/RFID card/WeChat/Alipay |
| Certification | |
| Safety & Compliance | CE & IEC |
5.Outlook
According to BNEF’s EV Charging Infrastructure Outlook 2025, over 4.8 million new charging stations will be deployed globally by 2030, with more than 60% of new installations featuring integrated storage and V2G capabilities, positioning charging infrastructure as a core component of the smart energy ecosystem.
As one of the core technologies driving the transition, Nepower holds significant future potential. It not only delivers ultra-fast charging for electric vehicles but also supports grid balancing and energy feedback, promoting greater integration of renewable energy and enhancing grid stability.
Contact us:
#Nebulaeletronics #EVCharger #V2G #DCCharger #SmartEnergy #Liquildcooling
Post time: Nov-14-2025